How does rub or marinade actually seep into meat?
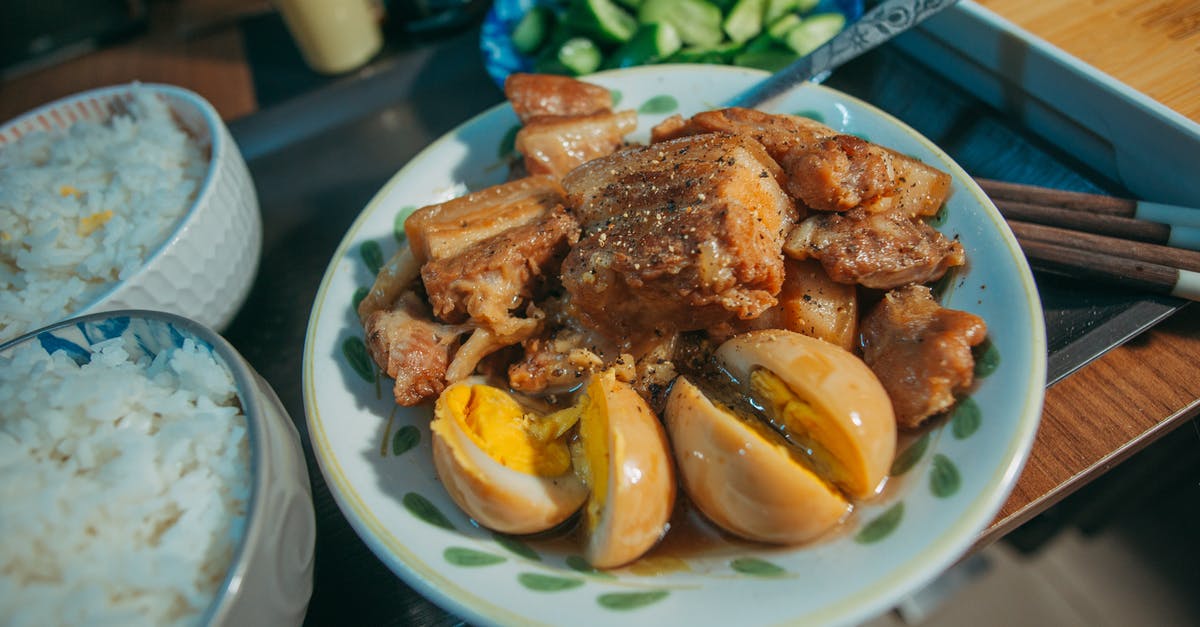

This morning I began crockpotting my first (ever) pork butt in an attempt to make pulled pork. In preparation of this, two days ago I smeared the meat with a spice rub and put it in a large sealed bag in the fridge. I did this because the recipe I was following stated that giving the rub a few days to "sink in" to the meat was crucial. This got me wondering:
Does rub/marinade actually penetrate into meat, if so, how?
The animal is dead, so I would imagine anything along the lines of "osmosis" or "capillary action", etc. would no longer be functioning.
To me, it doesn't seem feasible that rub/marinade would actually penetrate into a (dead) piece of meat. If it does, I'd like to know how, and how deep the rub/marinade actually travels.
Best Answer
Some of this has already been said briefly in comments and the previous answer, but since the question is interested specifically in chemical mechanisms, here are a few more details.
The general process to think about first is diffusion. This is part of a general physical property of systems to move to a state of equilibrium. Suppose you had a container with a wall in the middle and filled the one side with plain water and the other side with brine. If you remove the wall, you'd expect the solutions to mix -- the salt would diffuse into the plain water, and eventually the whole solution would be equally mixed.
When you place food into a solution which has higher concentrations of additives than the food itself, the additives migrate into the food to attain equilibrium. In porous food and meats, these additives may move far into the meat due to simple diffusion. For example, if you marinate fish, the larger openings between the muscle fiber will allow the marinade to seep deep into the meat. To a much lesser extent, this same process also happens in the outer layers of other kinds of meats (beef, pork, chicken), though the muscle fibers are so dense that this simple diffusion doesn't generally get very far.
Marinades can make a limited use of osmosis. Going back to our container example with two sides, osmosis is like replacing the wall with a barrier that has very tiny holes in it (technically known as a "semipermeable membrane"). Cell membranes (and for vegetable matter, cell walls) allow only certain small molecules to cross the membranes. (The reference in the question to living processes is only applicable to so-called active transport processes in cells, which require energy from the cell to power them. Osmosis, on the other hand, is a simple physical process of molecules moving through pores from higher concentration to lower concentration.)
Technically, osmosis is about a membrane equalizing concentration by allowing a solvent to cross the membrane while other (usually larger) molecules don't, and the most common solvent is water. As Jolene's experiment in comments shows, this process is mostly effective with small molecules that can "piggy-back" on this water motion, like salt. It's a little more complicated than that, since cell membranes also can selectively permit or deny travel based on water or fat solubility or whether a molecule is polar or not.
With both simple diffusion and osmosis processes, for deep penetration into the meat, tiny molecules will move much faster. It's not that some larger molecules can't penetrate the meat -- many of them do get into the surface layers. However, diffusion works through the random motion of vibrating molecules, and with all molecules at the same temperature, large molecules vibrate and move much more slowly. So it may take days, weeks, or even longer for large molecules to move an appreciable distance, and the meat would spoil and break down long before you get appreciable penetration.
(Note that besides size, another reason for slow penetration of other flavors is the low concentrations of these molecules. Whereas salt and sometimes other things like sugar can be highly concentrated in a brine or marinade, a concentrated solution of most other flavor components would be incredibly powerful and unpalatable. Without high concentrations, any diffusion or osmosis processes will be much slower.)
In terms of typical food additives, salt is the fastest traveling, but other less common additives (e.g., certain phosphates) also move relatively quickly. Sugar, once it is broken down into its simple components like glucose, will also move deeper into the meat, but more slowly than salt. (Note that some more complex sugars like table sugar, sucrose, can naturally break down in an acidic solution, but it's a slow process at room temperature or lower.)
But even when we say salt travels "fast," it will typically only go somewhere around 1" in 24 hours (depending on type of meat and concentration of brine). If you have a very large hunk of meat, you're unlikely to get full penetration even over the course of a couple days, so if you want full salt flavor throughout, your best bet is to cut up the meat into smaller chunks.
A dry rub with salt works in a similar way to a brine. (Some people actually call it "dry brining.") The only difference is that salt -- which is hydrophilic -- will initially attract molecules of water from the cell and even the air to dissolve on the surface. At that point, it becomes mobile and will use diffusion and osmosis to move into the meat just as above, just as it would in a brine or a marinade.
Aside from salt and a few other small molecules (e.g., simple sugars), most of the flavoring elements stay near the surface of the meat, typically the outer millimeter or two. In this outermost layer, certain elements in marinades may help to break down the outer cells and denature/dissolve proteins. Ingredients like acid, alcohol, and various natural enzymes (which can come from fruit juices or purees) will help to break down this outer layer. This process will allow deeper penetration of other flavors than would happen without such ingredients. So, instead of the flavors only going a fraction of a millimeter, some might get in as much as 1/8" or so. Acids and alcohols are also small molecules and can penetrate more deeply over time, but they will be more destructive to the cells as they move, leaving the outer layer of the meat mushy. For stewed meat or something like that, this is not an issue (and may actually be desirable); for meat that is meant to be roasted or grilled, long marinades in strong acid and/or alcohol may breakdown the meat too much.
It should be noted that some molecules (such as alcohols) can navigate the world between water-soluble and fat-soluble flavors, which may be helpful in some marinades. While water readily diffuses through into the outer layer of meat and can carry some larger flavor molecules with it, the same is not as true of oils and fat-soluble flavors. Essentially, part of a good marinade mix is choosing molecules that can "piggy-back" on each other to help move the flavors into the outer layer of the meat.
One final thing -- some people hold to a rigid division between "brining" (with salt) vs. "marinating" (which, to some people, by definition contains no salt). This arbitrary distinction has probably led to more ineffective marinating than anything else. It probably comes from the observation that salt will "dry out" meat, as in long-term meat preservation.
But when the meat is fresh (as most people who practice brining know), after the first hour or so, salt will actually draw water into meat. Yes, salt is hydrophilic and will draw some water out of meat initially, but as the salt diffuses into the meat, it disrupts proteins in the muscle fibers and causes some of the to dissolve. These changes then cause the cells to want to dissolve more water, so any water that may have left initially is then reabsorbed. In a brine or salty marinade, the weight of meat may increase by 10% or more due to brine moving into the meat (which leads to the well-known "juiciness" of brined meat). Along the way, many dissolved flavor components in the brine can "piggy-back" on this water moving into the meat, increasing the effectiveness and penetration of the marinade. Again, most of the bigger flavor components will remain in the surface layers, but you'll absorb more of them faster (and slightly deeper) with salt than without it.
To summarize for the specific case of a rub mentioned in the question: Especially if it contains salt, letting the rub sit for a day or two will allow much better penetration of the salt (and perhaps sugar and a few other small molecules). The other flavors won't move much more beyond the surface whether you wait an hour or a couple days. Without salt or another hydrophilic compound (like sugar) to get the "water flowing" and move dissolved compounds around, the dry rub is truly a surface feature, and you might as well apply it just before you cook the meat.
Pictures about "How does rub or marinade actually seep into meat?"


Quick Answer about "How does rub or marinade actually seep into meat?"
Marinades and Rubs are "surface treatments" only, they do not penetrate deeply into the meat. A brine is a deep treatment, which does penetrate by way of osmosis.Does dry rub penetrate meat?
A rub is an application of flavor at surface level that doesn't penetrate the meat too deeply or alter the cellular structure, but will season the protein and can add a fantastic crust or bark.How does a rub work on meat?
Rubs add flavor to the surface of the meat, and a good one may leave a bit of a crust after cooking. Marinades do double duty; they both flavor and tenderize meat. The tenderizing is the result of enzymes going to work on the protein strands.How do you make marinade penetrate meat?
This could be olive oil, sesame oil, yogurt, buttermilk, tahini or mayonnaise. Salt: Salt will help the water-soluble flavors in the marinade penetrate the tissues and remain behind after cooking. Salt also restructures the protein in the meat to create more gaps for moisture to fill in.How much of a marinade is absorbed?
About one-third of the marinade' sodium and calories will be absorbed. Many marinades are high in sodium, or salt. Many bottled marinades have 300 to 600 milligrams of sodium in each tablespoon. Even if only one-third is absorbed, that' 100 to 200 milligrams of sodium.Marinade VS Dry Rub on Steaks - What's Better? [Steak Experiment]
More answers regarding how does rub or marinade actually seep into meat?
Answer 2
Marinades and Rubs are "surface treatments" only, they do not penetrate deeply into the meat.
A brine is a deep treatment, which does penetrate by way of osmosis.
For a quick explanation of this see Alton Brown's Good Eats
Sources: Stack Exchange - This article follows the attribution requirements of Stack Exchange and is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0.
Images: FOX, Karolina Grabowska, Karolina Grabowska, Ryutaro Tsukata
